
I first heard the term zeta potential when reading The Forgotten Side of Medicine a while back.
I came across it again when republishing the interview with Dr Andrew Moulden.
I thought it time to produce something on the subject.
I like this subject because it is essentially an electrical concept, placed out of sight by the usual ignorance manufacturing systems, and more importantly it’s something that we can influence and take action to improve.
I have relied heavily on the magnificent work of A Midwestern Doctor.
Let’s start with an analogy.
Analogy
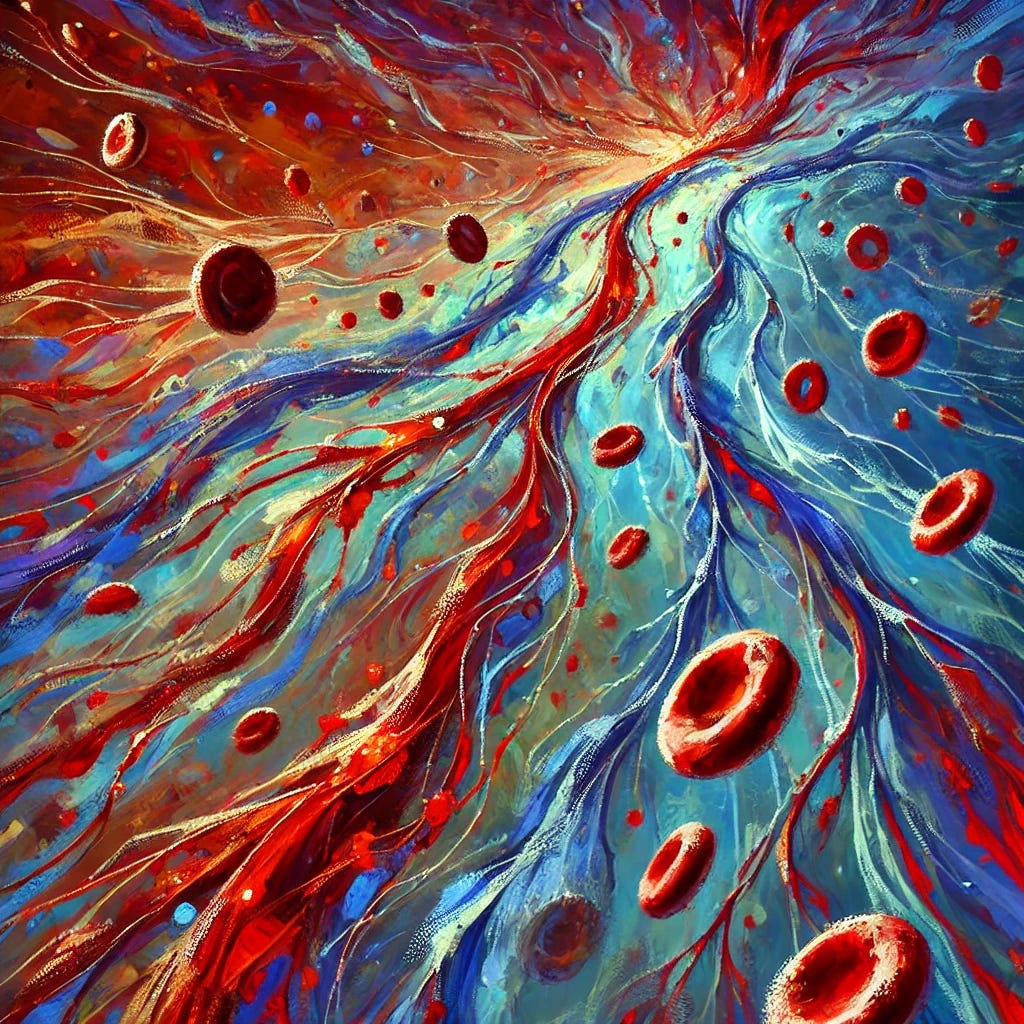
Imagine your body's circulatory system as a complex network of highways and streets. The blood cells are like cars traveling through this network. In a healthy system with good zeta potential, these "cars" have a slight negative charge, which acts like an invisible force field around each one. This charge keeps the cars repelled from each other, allowing them to flow smoothly through even the narrowest streets (capillaries) without clumping or causing traffic jams.
Now, think of factors that reduce zeta potential as if they're removing these force fields. Without them, the cars start to bump into each other and cluster together. This creates "traffic jams" in your blood vessels, especially in the smallest ones. These traffic jams can slow down or even block the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to various parts of your body, potentially leading to a wide range of health issues.
Just as a city functions best when traffic flows smoothly, your body operates optimally when blood and other fluids can circulate freely. Maintaining good zeta potential is like ensuring all the cars in your body have their force fields intact, allowing for smooth traffic flow and efficient delivery of essential resources throughout your body.
This analogy helps illustrate why zeta potential is so crucial for overall health and why factors that disrupt it (like certain environmental toxins, poor diet, or some medications) can have wide-ranging effects on the body.
25 Questions & Answers
Question 1: What is zeta potential and how does it relate to colloidal suspensions?
Zeta potential refers to the charge difference between water ions coating charged particles and the surrounding water in a colloidal suspension. It's a key factor in determining colloidal stability. When particles are placed in water, they can form a colloidal suspension where each particle is repelled from others and evenly distributed. The degree of this repulsion, largely determined by zeta potential, affects whether particles will remain suspended or clump together.
In colloidal systems, zeta potential is the easiest factor to control when trying to improve or reduce colloidal dispersion. When zeta potential is no longer sufficient to overcome attractive forces in a colloidal system, particles begin to clump together, first in small agglomerations and then in larger clumps as zeta potential worsens.
Question 2: How does aluminum affect zeta potential and why is this significant?
Aluminum is one of the most effective agents for reducing zeta potential. It's frequently used in sewage plants to separate organic matter from water and in wound treatment to clot blood. The significant impact of aluminum on zeta potential is concerning because it's widely used in vaccines as an adjuvant, in municipal water systems, and in various food products and cookware.
The use of aluminum in vaccines may account for many of their side effects, as it can cause blood sludging and impair microcirculation. This effect extends to other aluminum exposures, such as cooking in aluminum pans or drinking from aluminum cans, which can significantly impair microcirculation and potentially lead to health issues.
Question 3: What are the key factors that influence zeta potential in the human body?
Several factors influence zeta potential in the human body:
Diet: High sodium intake relative to potassium can impair zeta potential.
Environmental toxins: Aluminum and other heavy metals can significantly reduce zeta potential.
Infections: Many pathogens carry positive charges that disrupt zeta potential.
Medications: Some pharmaceuticals, particularly those containing aluminum, can negatively impact zeta potential.
EMFs: Electromagnetic fields may affect zeta potential, though this is less well-established.
Additionally, factors like dehydration, lack of movement, and aging can all contribute to reduced zeta potential in the body. The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining zeta potential by excreting harmful cations, but their function can decline with age or disease.
Zeta potential is fundamentally an electrical concept. It refers to the electrical potential difference between the bulk of a liquid and the stationary layer of fluid attached to a dispersed particle.
Question 4: How does zeta potential relate to blood flow and circulation?
Zeta potential plays a crucial role in blood flow and circulation. Blood is a colloidal suspension of cells in plasma, and its ability to flow smoothly depends on maintaining proper zeta potential. When zeta potential is impaired, blood cells can begin to clump together, a process known as blood sludging. This can lead to reduced blood flow, especially in small capillaries, potentially causing microstrokes and other circulatory problems.
The body maintains blood zeta potential near the agglomeration threshold to allow for clotting when needed (such as during injury), but this also makes it vulnerable to factors that can push it over this threshold. Impaired zeta potential in blood can lead to various circulatory issues, including heart arrhythmias, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems.
Question 5: What role do the kidneys play in maintaining zeta potential?
The kidneys play a vital role in maintaining physiological zeta potential. Their primary function in this regard is to excrete cations (positively charged ions) that can destroy zeta potential. During periods of excess cation load, such as after consuming salty foods, the kidneys work in overdrive to correct zeta potential by boosting their excretion of dangerous cations like aluminum.
As individuals age, the kidney's ability to maintain zeta potential declines. This decline makes older people more susceptible to sudden influxes of positive charges and may contribute significantly to the aging process. Some researchers believe that a primary cause of aging is the gradual loss of the kidney's function to maintain zeta potential.
Question 6: How do infections and microbes impact zeta potential?
Infections and microbes can significantly impact zeta potential in several ways. Many pathogenic organisms carry a positive charge, which allows them to adhere to negatively charged cells in the body. This positive charge can disrupt the overall zeta potential of the system. Additionally, bacterial metabolism of proteins can lower their zeta potential through decarboxylation reactions, which remove negative charges from proteins.
During acute infections, a decrease in physiologic zeta potential is consistently observed. This phenomenon helps explain why elderly individuals, who often have lower baseline zeta potential, are more vulnerable to infections like influenza. The body's struggle to eliminate certain microorganisms, particularly smaller ones like mycoplasma, can lead to chronic kidney conditions and ongoing disruption of zeta potential.
Zeta potential can be measured and described by a number. It's typically measured in millivolts (mV). The scale generally ranges from about -100 mV to +100 mV, though most biological systems tend to be in the negative range.
Question 7: What is the relationship between zeta potential and aging?
The relationship between zeta potential and aging is multifaceted. As individuals age, their ability to maintain proper zeta potential often declines, primarily due to decreased kidney function. The kidneys play a crucial role in excreting cations that can disrupt zeta potential, and this function tends to diminish with age.
Additionally, aging is associated with a decline in albumin levels, which is an important stabilizing colloid in the blood. Lower albumin levels can further compromise zeta potential. Some researchers believe that the gradual loss of the body's ability to maintain zeta potential is a primary cause of aging. Interestingly, some pioneers in zeta potential research have demonstrated that many complications of aging, including cognitive decline, can be reversed by restoring physiologic zeta potential.
Question 8: How do vaccines potentially impact zeta potential?
Vaccines can potentially impact zeta potential in several ways. Many vaccines contain aluminum as an adjuvant, which is highly effective at reducing zeta potential. This property of aluminum may explain why it's such an effective adjuvant, as it mimics a common characteristic of pathogenic organisms and likely triggers the innate immune system.
Additionally, the immune stimulation caused by vaccines can lead to white blood cell migration into capillaries, potentially obstructing blood flow in these small vessels. This process, combined with the reduction in zeta potential, can lead to varying degrees of microcirculatory impairment. The cumulative effect of multiple vaccinations may progressively worsen microcirculation until a critical threshold is reached where severe injury occurs.
Question 9: What is the Moulden Anoxia Spectrum Syndromes (MASS) and how does it relate to zeta potential?
The Moulden Anoxia Spectrum Syndromes (MASS) refers to a process observed by Dr. Andrew Moulden where white blood cells migrate to certain capillaries during an immunostimulatory event, such as vaccination. Because white blood cells are much larger than red blood cells, their presence in capillaries can block blood flow, especially if blood sludging is already occurring due to reduced zeta potential.
MASS works in conjunction with reduced zeta potential to potentially cause harm following vaccinations. The combination of reduced zeta potential (causing blood sludging) and white blood cell obstruction in capillaries can lead to microstrokes and other circulatory impairments. This dual mechanism helps explain the variability in vaccine injuries and why vaccine damage can be cumulative.
Directly measuring an individual's zeta potential is not typically done in clinical settings. However, there are indirect ways to assess it:
Observing blood flow in the eyes (conjunctival vessels) using specialized microscopy.
Analyzing the electrical conductivity of urine, which can indicate how well the kidneys are excreting cations that affect zeta potential.
Assessing overall health markers that are associated with good zeta potential, such as cardiovascular health and microcirculation.
Question 10: How does diet, particularly sodium and potassium intake, affect zeta potential?
Diet plays a significant role in maintaining proper zeta potential, with the balance between sodium and potassium being particularly important. Modern diets often contain much more sodium than potassium, which is a reversal from our evolutionary past. This imbalance can contribute to poor zeta potential because sodium is more likely to disrupt physiologic zeta potential than potassium.
Riddick and subsequent researchers advocated for eating more fresh produce (which retains its potassium), substituting potassium chloride for sodium chloride in seasoning, and reducing the frequency of eating at restaurants. They observed that a single restaurant meal could significantly stagnate the system in individuals with zeta potential impairment. Additionally, excessive fat intake and alcohol consumption were noted to potentially induce intravascular coagulation.
Question 11: What are some methods for improving or restoring zeta potential in the body?
Several methods have been identified for improving or restoring zeta potential in the body:
Consuming anionic dispersants: Potassium citrate mixed with sodium or potassium bicarbonate in distilled water has been found effective.
Using magnesium sulfate: Either through Epsom salt baths or intravenous administration.
Pharmaceutical dispersants: Heparin and EDTA can be used, though EDTA must be carefully dosed and administered.
Drinking de-ionized water: Distilled or reverse osmosis water can help maintain zeta potential.
Avoiding harmful cations: Reducing exposure to aluminum and other positive ions in food and environment.
Oxidative therapies: Treatments like ozone therapy, IV vitamin C, and ultraviolet blood irradiation may help.
These approaches aim to either add beneficial negative charges, remove problematic positive charges, or disperse areas of fluid stagnation in the body.
Question 12: How does zeta potential relate to protein folding and misfolding?
Zeta potential plays a crucial role in protein folding and stability. Proteins, when synthesized, form complex three-dimensional structures that are essentially colloidal suspensions. The stability of these structures depends on the same factors that influence colloidal stability, including zeta potential.
Ions that disrupt zeta potential can cause protein misfolding or denaturing. This relationship may explain why aluminum is associated with Alzheimer's disease, as Alzheimer's plaques are misfolded proteins often found with aluminum. Similarly, the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein's association with protein misfolding diseases like amyloidosis and prion diseases may be related to its effect on zeta potential. The rapid misfolding of blood clotting proteins in spike protein-affected individuals could also be a consequence of zeta potential disruption.
In the context of biological systems, a more negative zeta potential is generally considered better. For red blood cells, a normal zeta potential is around -15.7 mV. A more negative value (e.g., -20 mV) would indicate better colloidal stability, meaning blood cells are less likely to clump together.
However, it's important to note that "higher" in this case means more negative. A zeta potential of -20 mV would be considered "higher" or better than -10 mV, even though -20 is a lower number in absolute terms.
It's also crucial to understand that there's an optimal range. Extremely high (very negative) or low (positive) zeta potentials can both be problematic. The goal is to maintain a physiologically appropriate negative zeta potential that allows for proper blood flow and cellular function.
Question 13: What is the connection between zeta potential and liquid crystalline water?
Liquid crystalline water and zeta potential are closely interconnected, though the exact nature of their relationship is still being understood. Liquid crystalline water forms on negatively charged surfaces and has a negative charge itself. This property aligns with the negative charge necessary for maintaining proper zeta potential in biological systems.
Many factors that improve zeta potential also seem to increase the presence of liquid crystalline water in the body, and vice versa. For example, infrared light exposure can increase both liquid crystalline water formation and zeta potential. However, there are cases where the effects on liquid crystalline water and zeta potential may differ, highlighting the complexity of their relationship.
Question 14: How do oxidative therapies potentially impact zeta potential?
Oxidative therapies, such as ozone therapy, IV vitamin C, and ultraviolet blood irradiation, may positively impact zeta potential by neutralizing positive charges in the body. These therapies can oxidize and neutralize positively charged pathogens or other harmful molecules that disrupt zeta potential.
For instance, ozone therapy has been observed to rapidly normalize vital signs in critically ill patients, possibly by oxidizing the positive charge of the spike protein in the blood, thereby restoring zeta potential. This restoration allows blood to declump, improving tissue perfusion and oxygenation. However, the effectiveness of these therapies can vary depending on the stage of illness and the individual's overall health status.
Question 15: What is the relationship between EMFs and zeta potential?
The relationship between electromagnetic fields (EMFs) and zeta potential is an area of ongoing research and debate. Some studies suggest that EMFs, particularly those from Wi-Fi routers and other electronic devices, may negatively impact zeta potential and liquid crystalline water in the body.
For example, Pollack found that Wi-Fi routers can shrink exclusion zone water (a form of liquid crystalline water) by 10-15%. Additionally, some researchers have observed that EMFs can cause blood cells to clump together, suggesting a disruption in zeta potential. However, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and extent of EMF effects on zeta potential and overall health.
Question 16: What is liquid crystalline water and how does it relate to zeta potential?
Liquid crystalline water is a phase of water that forms when water molecules align into a structured, semi-solid state. It typically forms on negatively charged surfaces and in the presence of ambient energy, often infrared light. This water phase has unique properties, including the ability to exclude solutes and create barriers within biological systems.
The relationship between liquid crystalline water and zeta potential is complex. Both are influenced by similar factors, such as charge distribution and the presence of certain ions. Liquid crystalline water often forms a protective layer around colloidal particles, potentially contributing to their dispersion and stability - a key aspect of zeta potential. However, excessive liquid crystalline water can also increase viscosity, which is associated with poor zeta potential. The balance between these effects likely plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal physiological conditions.
Question 17: How do sunlight and infrared light affect zeta potential and liquid crystalline water?
Sunlight and infrared light play significant roles in the formation of liquid crystalline water and potentially in maintaining zeta potential. Infrared light, particularly at wavelengths around 3000 nm, has been shown to significantly increase the production of liquid crystalline water in the body. Sunlight exposure has multiple benefits related to this topic:
It produces cholesterol sulfate, which helps maintain cell membrane stability and zeta potential.
It generates nitric oxide, improving cardiovascular health and circulation.
It directly creates liquid crystalline water in the body.
These effects may explain some of the health benefits attributed to sunlight exposure beyond vitamin D production. Conversely, blue light (from screens and modern lighting) has been found to shrink liquid crystalline water, potentially negatively impacting zeta potential.
Question 18: What is the Hofmeister series and how does it relate to zeta potential?
The Hofmeister series, developed by Franz Hofmeister in 1888, ranks various ions based on their ability to stabilize or denature proteins in solution. Interestingly, this series closely aligns with the relative effects of specific ions on zeta potential. The series typically organizes ions from those that stabilize colloids (and improve zeta potential) to those that destabilize colloids (and worsen zeta potential).
For example, phosphate and citrate ions, which are on the stabilizing end of the Hofmeister series, are also effective at improving zeta potential. Conversely, aluminum ions, which are on the destabilizing end, are highly effective at reducing zeta potential. This correlation between the Hofmeister series and zeta potential effects provides insight into how different ions interact with biological systems and influence colloidal stability.
Question 19: How do anesthetics impact liquid crystalline water and zeta potential?
Anesthetics have been found to disrupt liquid crystalline water rather than create it. They do this by forming clathrates (pockets of water) around themselves, preventing that water from existing in a liquid crystalline phase. Additionally, some anesthetics, like lidocaine, have been observed to make the surface charge of biological membranes more positive, potentially impacting zeta potential.
Interestingly, anesthetics also affect the transition temperature of cell membranes between gel and liquid states. The degree to which an anesthetic can shift this transition temperature correlates directly with its potency. This relationship further supports the link between liquid crystalline water, phase transitions, and the function of anesthetics, highlighting the complex interplay between these factors in biological systems.
Question 20: What is the role of stabilizing colloids like albumin in maintaining zeta potential?
Stabilizing colloids, particularly albumin, play a crucial role in maintaining zeta potential in biological systems. Albumin, the most abundant protein in blood plasma, helps maintain colloidal stability and prevent blood sludging. Riddick's experiments showed that albumin could significantly protect the blood system against coagulation.
As people age, their albumin levels tend to decrease, which correlates with an increased risk of disability and mortality. This decline in albumin may contribute to the age-related deterioration of zeta potential. Maintaining adequate albumin levels through proper nutrition and digestion may therefore be important for preserving zeta potential and overall health, especially in older individuals.
Question 21: How does earthing potentially affect zeta potential?
Earthing, also known as grounding, involves electrically connecting oneself to the Earth's surface. This practice has been found to potentially improve zeta potential in the body. The Earth's surface carries a negative charge, and when a person is grounded, this charge may be transferred to the body, helping to restore the physiologic negative charge within.
A study has directly demonstrated that earthing can improve zeta potential in the blood. Many of the reported benefits of earthing, such as improved sleep and reduced inflammation, align with what would be expected from improved zeta potential. Some individuals have reported improvements in conditions like Raynaud's syndrome and even COVID-19 vaccine injuries after practicing earthing, further suggesting its potential impact on zeta potential and overall health.
Question 22: What is thixotropy and how does it relate to blood flow and zeta potential?
Thixotropy is a property of colloids that states they are more likely to retain their colloidal dispersion (not clump together or thicken) when they are moving. This principle has important implications for blood flow and zeta potential in the body. When fluids in the body become stagnant, they are more likely to clump together, potentially leading to health issues.
Activities that create motion in the body, such as exercise or certain manual therapies, can help break up these fluid agglomerations and maintain proper colloidal dispersion. This is why movement is often recommended for maintaining circulatory health and potentially for reducing the risk of blood clots. Understanding thixotropy helps explain why fluid movement is so crucial for maintaining health and proper zeta potential throughout the body.
Question 23: How do EMFs and 5G potentially impact zeta potential and health?
The potential impact of electromagnetic fields (EMFs) and 5G technology on zeta potential and health is a topic of ongoing research and debate. Some studies have suggested that EMFs can negatively affect zeta potential and liquid crystalline water in the body. For instance, Wi-Fi routers have been observed to shrink exclusion zone water by 10-15%, and some researchers have reported EMFs causing blood cells to clump together, indicating a possible disruption of zeta potential.
Individuals with complex illnesses that may be linked to reduced zeta potential (such as chronic migraines or Lyme disease) often report sensitivity to EMFs. Some practitioners recommend reducing EMF exposure through measures like using low-EMF devices, avoiding Wi-Fi at night, or using EMF shielding. However, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and extent of EMF effects on zeta potential and overall health.
Question 24: What are some proposed treatments or therapies for improving zeta potential?
Several treatments and therapies have been proposed for improving zeta potential:
Zeta Aid: A mixture of potassium citrate and bicarbonate in deionized water.
Magnesium sulfate: Used in Epsom salt baths or intravenously.
EDTA chelation therapy: When properly dosed and administered.
Oxidative therapies: Such as ozone therapy, IV vitamin C, and ultraviolet blood irradiation.
Earthing: Electrically connecting to the Earth's surface.
Dietary changes: Increasing potassium intake relative to sodium, consuming stabilizing colloids like egg whites.
Infrared light exposure: Through sunlight or infrared saunas.
Proper hydration: Using deionized water (distilled or reverse osmosis).
Reducing exposure to harmful cations: Especially aluminum.
Addressing chronic infections: Which can disrupt zeta potential.
These approaches aim to either add beneficial negative charges, remove problematic positive charges, or disperse areas of fluid stagnation in the body.
Question 25: How might zeta potential relate to COVID-19 and spike protein injuries?
Zeta potential may play a significant role in COVID-19 and spike protein injuries. The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein has been observed to directly impair blood cell zeta potential, leading to blood clumping. This effect could explain many of the circulatory and inflammatory issues seen in severe COVID-19 cases and in some individuals after vaccination.
Treatments that improve zeta potential, such as ivermectin or certain oxidative therapies, have shown promise in treating COVID-19, possibly by dispersing blood cells that have clumped together due to spike protein exposure. Additionally, some of the long-term effects of COVID-19 and reported vaccine injuries, such as fatigue, cognitive issues, and circulatory problems, align with what might be expected from chronic zeta potential impairment. Understanding and addressing zeta potential could therefore be crucial in developing effective treatments for these conditions.
References
What is the Relationship Between Liquid Crystalline Water and Zeta Potential?
How to Improve Zeta Potential and Liquid Crystalline Water Inside the Body
Why Do All Vaccines Cause Harm?
What Makes All Vaccines So Dangerous?
I appreciate you being here.
If you've found the content interesting, useful and maybe even helpful, please consider supporting it through a small paid subscription. While everything here is free, your paid subscription is important as it helps in covering some of the operational costs and supports the continuation of this independent research and journalism work. It also helps keep it free for those that cannot afford to pay.
Please make full use of the Free Libraries.
Unbekoming Interview Library: Great interviews across a spectrum of important topics.
Unbekoming Book Summary Library: Concise summaries of important books.
Stories
I'm always in search of good stories, people with valuable expertise and helpful books. Please don't hesitate to get in touch at unbekoming@outlook.com
For COVID vaccine injury
Consider the FLCCC Post-Vaccine Treatment as a resource.
Baseline Human Health
Watch and share this profound 21-minute video to understand and appreciate what health looks like without vaccination.















Excellent stack… I found using PEMF devices helpful along with your suggestions…. they simply use magnetic pulses to make polarity switching between blood cells thereby reducing roulette stacking…stop carrying mobile phones in pockets nearer your skin or switch them into airplane mode… keep your distance from microwave ovens when in use… all forms of EMF can disrupt the zeta potential…. Electric cars are a case in point.
Great article. I learn so much from Unbekoming interviews and the commenters here. This article helped to fill in the gaps and the timeline as to what caused the death of my mother. The final piece I needed to understand how she was taken out so quickly and deadly after a lifetime of good health. I know it sound macabre but I need to come to terms in understanding how and why I lost her. This article helped me in that search for understanding.