Vaccinations: How Vaccines Wreck Immunity (2015)
By Dr Jack & Mary Stockwell – 30 Q&As – Unbekoming Book Summary
I think it is a rational decision for a parent to say, I know that giving my child a chicken pox vaccine will turn their immune system backwards, it will shift them toward allergies, autoimmune diseases, and even cancer. I know it will create some neurotoxicity…but I am just not willing to face the chance of them getting chicken pox. Fine.
What I don’t like is the health department, the hospitals, pediatricians saying vaccines work great and there is no downside. Hogwash. I mean that’s a fairy tale. So long as parents and adults know both sides of the story, they can make their own decision.
Dr Thomas Cowan
I’ll keep writing about childhood vaccination poisoning for as long as this Substack continues. Ultimately, it comes down to one decision: whether a parent will inject their child, at birth, or not. That’s the ultimate sliding door moment.
Remember, the first injection is not a vaccine but a “vitamin,” and it all starts with saying no to that “vitamin.”
I did inject, because I was brainwashed, and I didn’t wake up from that coma until the damage was already done. But I suppose one of the unintended gifts of the shock and awe of Operation Lockstep is that it has shaken me—and millions of others—out of our deep sleep.
We now know that the unvaccinated, few that they are, are healthier than the vaccinated in every way that can be measured.
Most books on this subject tend to add yet another layer of insight to my growing understanding of the evils of poisoning children through vaccination. This book does a solid job of explaining the role of T-cells and B-cells, as well as why Cartel Medicine needs to rely on aluminium adjuvants.
For someone entirely new to the topic, it’s a concise and effective introduction.
With thanks to Dr Jack and Mary Stockwell.
How Vaccines Wreck Human Immunity: Stockwell CGP, Dr. Jack, Stockwell CGP, Mary
Related Posts
Deep Dive Conversation Library (Bonus for Paid Subscribers Only)
This deep dive is based on the book’s contents.
Discussion No.26:
20 important insights from “How vaccination wrecks human immunity”
Thank you for your support.
Analogy
Imagine a master orchestra that has played together for thousands of years. Each musician knows exactly when to play their part, how to complement others, and how to create beautiful harmony. The conductor (your immune system) has perfected the timing of each instrument's entry and exit, creating not just music, but a masterpiece of coordination.
Now imagine someone decides this process takes too long and seems inefficient. They decide to "improve" the orchestra by removing the first half of the symphony and forcing the second half to play without hearing what came before. They use artificial means to make the musicians play louder and faster, believing this creates the same end result more quickly. While this might produce sound that seems similar on the surface, it fundamentally disrupts the musical harmony and timing that made the original performance special.
The more they "improve" the orchestra this way, the more the musicians lose their natural sense of timing and coordination. Some begin playing at the wrong times, others play too aggressively, and a few even start playing against their fellow musicians. What was once a self-regulating, harmonious system becomes increasingly chaotic and discordant.
This mirrors how vaccination attempts to shortcut the body's natural immune response by skipping the T-cell "opening movement" and forcing B-cells to play their part without proper context. Just as you can't create a true musical masterpiece by shortcuts and artificial stimulation, you can't replicate the sophistication of natural immunity through artificial means without potentially disrupting the entire system.
The book argues that just as we would never consider "improving" a great orchestra by forcing it to skip movements and play out of sequence, we should think carefully about interventions that fundamentally alter the body's natural immune "symphony" that has been perfected over millennia of evolution.
12-point summary
1. Natural Immune Architecture: The human immune system consists of three interconnected types of immunity - infant, innate, and acquired immunity. This sophisticated system evolved over thousands of generations to work in precise sequence, with T-cells leading the response and B-cells following to create long-term protection. This natural architecture demonstrates remarkable effectiveness when allowed to function as designed.
2. Vaccination's Fundamental Problem: Vaccines attempt to generate immunity by bypassing the natural T-cell response and artificially stimulating B-cell antibody production. This shortcut requires neurotoxic adjuvants like mercury and aluminum to force an immune response to dead or weakened pathogens. This disruption of natural immune sequencing contributes to the dramatic rise in autoimmune conditions since the 1940s.
3. Historical Disease Patterns: Statistical evidence shows that major infectious diseases, including polio, diphtheria, and measles, were already declining significantly before vaccine introduction. These declines correlate more strongly with improvements in sanitation, nutrition, and public health measures than with vaccination programs. This challenges the conventional narrative about vaccines' role in disease elimination.
4. The Autoimmune Explosion: Before 1940, autoimmune diseases were virtually unknown. Since then, over 80 different autoimmune conditions have been identified, affecting millions of people. This timing coincides with the widespread implementation of vaccination programs, suggesting a possible connection between disrupted immune responses and autoimmune dysfunction.
5. The Role of Symptoms: Fever, inflammation, and other disease symptoms represent the body's intentional healing responses rather than problems requiring suppression. These symptoms indicate proper immune system function, with the body orchestrating complex responses to eliminate threats and restore health. Modern medicine's approach of suppressing these symptoms may interfere with natural healing processes.
6. The Microbial Partnership: Humans evolved to live in cooperation with viruses and other microorganisms, not in constant battle against them. Every viral infection may serve a beneficial purpose, acting as a cleanser or purger to remove harmful substances from the body. This understanding challenges the current medical paradigm of pathogen elimination.
7. Childhood Health Crisis: Modern children face unprecedented rates of chronic illness, with 20-40% suffering from ongoing health conditions. This represents a dramatic shift from previous generations when chronic childhood illness was rare. The book connects this change to increased vaccination schedules, environmental toxins, and disrupted natural immune development.
8. Medical System Transformation: The medical industry has shifted from producing healers to creating "chemical interventionists," prioritizing symptom management over addressing root causes. This transformation reflects pharmaceutical industry influence over medical education and practice, creating a system that profits from ongoing illness rather than prevention and cure.
9. Research Gap Reality: Despite decades of vaccine use, no proper long-term studies compare health outcomes between vaccinated and unvaccinated populations. This absence of comprehensive research raises questions about the scientific basis for current vaccination practices and their long-term effects on human health.
10. Infant Immunity Timing: Babies cannot produce their own antibodies until around twelve months of age, relying instead on maternal antibodies for protection. This biological fact raises concerns about the practice of administering vaccines during early infancy when the immune system is still developing.
11. Environmental Impact: The combined effects of environmental toxins, poor nutrition, and medical interventions create unprecedented challenges for human immune systems. This total burden may overwhelm natural defense mechanisms, particularly during critical developmental periods.
12. Natural Health Solution: Supporting rather than suppressing the body's innate healing capabilities offers a more effective approach to health. This includes providing proper nutrition, allowing natural immune responses to run their course, and being more selective about medical interventions that might disrupt natural immunity.
30 Questions & Answers
1. How do T-cells and B-cells work differently in the immune response process?
T-cells function as the first line of active defense in the immune response, recognizing viruses and bacteria as antigens and attacking them directly on contact. These cells act swiftly and decisively, without hesitation, creating what we observe as pus in an infection - a combination of both dead invaders and expended T-cells. Working through the thymus gland for training, T-cells operate as efficient eliminators without any political or moral constraints; they simply identify and neutralize threats.
B-cells, by contrast, operate more like intelligence agencies, observing and documenting T-cell activities from a distance. They don't engage in direct combat but instead produce antibodies based on chemical messages received from T-cells. This backup system creates a biological memory that activates faster if the same threat appears again. The process takes 14-28 days for B-cells to manufacture antibodies, but once formed, they provide lifetime immunity against specific pathogens.
2. What is the significance of the three types of immunity mentioned in the book, and how do they interact?
Infant immunity represents the first layer of protection, transferred from mother to child around the twentieth week of pregnancy through the placental barrier. This immunity is crucial because infants cannot produce their own antibodies until approximately twelve months of age. These maternal antibodies float in the infant's bloodstream, ready to protect against pathogens during the vulnerable first months of life.
Innate immunity operates continuously in the background as a 24/7 defense system, while acquired immunity develops through exposure to specific pathogens. The innate system includes phagocytes patrolling the blood and lymph, along with stomach acid and skin pH barriers. Acquired immunity, also called humoral immunity, represents the learning and adapting component that develops specific defenses against encountered pathogens, creating long-term protection through antibody production.
3. Why do infants lack the ability to create antibodies until around 12 months of age?
The book explains this biological limitation as a natural part of human development, where infants rely entirely on their mother's antibodies passed through the placental barrier during pregnancy. This transfer occurs during the second trimester of development, around the twentieth week, providing protection when the infant's system is still developing. During this time, the infant's body remains sterile and protected within the womb.
This arrangement ensures survival during the critical early months of life while the infant's immune system matures. The maternal antibodies begin decreasing around six months as the infant's own immunity strengthens, creating a gradual transition to self-sufficiency. This explains why infectious diseases rarely affect infants in their first six months unless this natural process gets disrupted by external influences like antibiotics, medications, or vaccines.
4. What role do adjuvants play in vaccines, and why are they necessary according to the book?
Adjuvants serve as chemical shock agents in vaccines, forcing the immune system to recognize and respond to dead or attenuated viruses that it would otherwise ignore. The book explains that without these chemical additives, the body's immune system would have no natural reaction to the killed or weakened viral material in vaccines, as the immune system has evolved to respond only to live threats.
These substances, including mercury, aluminum, and formaldehyde, function not as preservatives but as neurological irritants that provoke an artificial immune response. The book emphasizes that calling mercury a preservative misrepresents its true purpose - it acts as a neurotoxic agent deliberately included to force an unnatural immune reaction, similar to describing cyanide as a preservative.
5. How does the book explain the relationship between fever and healing?
Fever represents the body's intentional immune response rather than a symptom of disease that needs suppression. The book describes how the liver deliberately increases body temperature as part of a coordinated defense strategy to destroy invading pathogens, working alongside other immune responses like inflammation and increased mucus production.
This perspective challenges the common medical approach of fever reduction, suggesting instead that fever serves as a crucial component of the healing process. The book positions fever as one of several beneficial bodily responses, including vomiting, diarrhea, and inflammation, all working together to eliminate threats and restore health rather than being problems that require medical intervention.
6. What evidence does the book present regarding disease decline before vaccine introduction?
The book provides statistical evidence through graphs showing that diseases like polio, diphtheria, and measles were already experiencing significant decline before their respective vaccines were introduced. These declines, documented in both Australian and United States records, demonstrate up to 90% reduction in disease rates prior to vaccination programs, with specific emphasis on polio's dramatic decrease before the Salk and Sabin vaccines appeared in 1955 and 1959.
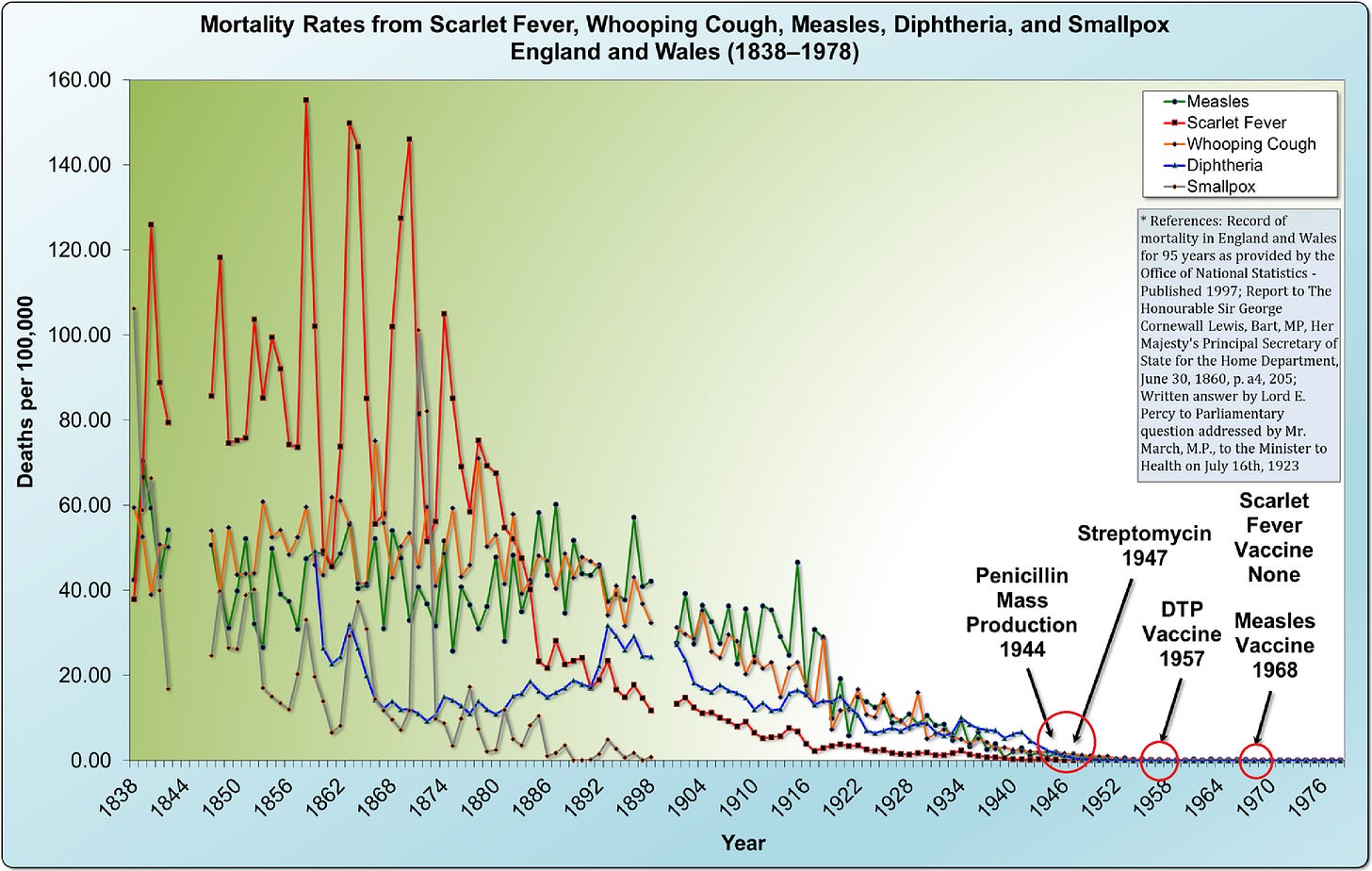
Dr. Andrew Weil's quoted explanation attributes these declines to improvements in sanitation, sewage disposal, and food and water distribution systems rather than medical interventions. The book uses this historical data to challenge the conventional narrative that vaccines were primarily responsible for eliminating these diseases, suggesting instead that public health measures played a more significant role.
7. How does the book explain the connection between sugar consumption and polio?
The book presents a compelling case study from South Carolina in the early 1950s, where the state government called for a voluntary reduction in sugar consumption among its citizens. Following this dietary intervention, the state reportedly experienced an immediate 90% reduction in polio cases, suggesting a direct correlation between sugar intake and polio susceptibility.
This connection challenges the traditional narrative about polio transmission and prevention, indicating that dietary factors played a more significant role in disease susceptibility than commonly acknowledged. The book uses this historical example to demonstrate how nutritional approaches to disease prevention might have been overlooked in favor of pharmaceutical interventions.
8. What is the significance of the 1940s as a turning point in autoimmune diseases?
The 1940s marked a pivotal shift in human health patterns, with the book identifying this decade as the beginning of an "explosion" in autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative conditions, digestive dysfunction, cardiopulmonary disease, and cancer. This period coincides with the widespread introduction of vaccination programs and represents a fundamental change in how the human immune system interacts with pathogens.
Prior to the 1940s, autoimmune diseases were virtually unknown, yet they have become increasingly prevalent since then. The book attributes this dramatic increase to the modification of natural immune responses through vaccination practices, particularly the bypassing of cell-mediated immunity in favor of artificial antibody production, leading to what it describes as an "upside down" immune response where the body attacks itself rather than external threats.
9. How does the book explain the dramatic increase in autism rates over recent decades?
The book presents stark statistics showing autism rates increasing from one in 10,000 two decades ago to current rates as high as one in 22 in some areas. This dramatic escalation is presented alongside concerns about vaccination practices and their potential impact on neurological development, with predictions suggesting rates could reach one in two by 2020 if trends continue.
The exponential increase in autism rates is positioned within a broader context of rising childhood chronic illnesses and autoimmune conditions that emerged after the 1940s. While the book doesn't claim direct causation, it associates these increases with changes in medical practices, particularly the introduction of multiple childhood vaccinations and their accompanying neurotoxic adjuvants.
10. What is the fundamental difference between natural immunity acquisition and vaccine-induced immunity?
Natural immunity follows a specific sequence where T-cells first encounter and fight the pathogen (cell-mediated immunity), followed by B-cells producing antibodies based on this encounter (humoral immunity). This two-step process results in lifetime immunity and allows the body to develop a complete, coordinated immune response that includes both immediate protection and long-term memory.
Vaccine-induced immunity, conversely, bypasses the T-cell response and artificially stimulates B-cell antibody production through chemical adjuvants. The book argues this shortcut disrupts the natural order of immune response, potentially leading to incomplete or improper immunity and requiring booster shots to maintain protection. This artificial approach fails to provide the comprehensive immunity that natural exposure creates and may contribute to broader immune system dysfunction.
11. How does the book describe the historical shift in medical education and practice since the 1940s?
Medical education transformed from producing healers to creating what Dr. Royal Lee terms "chemical interventionists." This fundamental shift occurred as pharmaceutical companies gained influence over medical school curricula, establishing a standard of care that predominantly relies on chemical solutions rather than addressing root causes of illness. The education system began training doctors to manage symptoms through medication rather than support the body's natural healing processes.
The book points to this period as when medicine moved away from prevention and holistic understanding of health. Drawing a stark contrast with historical Oriental medicine, where doctors were paid to keep patients healthy and received no compensation when patients fell ill, the modern Western system creates financial incentives around treating illness rather than maintaining health. This shift fundamentally altered how physicians approach patient care and understand disease processes.
12. What critique does the book offer regarding the pharmaceutical industry's influence on medical practice?
The pharmaceutical industry's influence extends beyond medication development into the very structure of medical practice, according to the book. Through campaign contributions, lobbying efforts, and control over medical education, pharmaceutical companies have established a system where natural healing approaches face legal restrictions while chemical interventions receive official sanction. The book specifically highlights how companies like Standard Process faced FDA restrictions for natural supplements while tobacco companies received approval for marketing cigarettes as digestive aids.
This influence has created what the book describes as a "business called Health Care" rather than a healing profession. The system profits from ongoing illness management rather than cure or prevention, leading to a situation where effective natural treatments face suppression while potentially harmful chemical interventions receive promotion. The book suggests this creates a conflict between public health interests and industry profit motives.
13. How does the book explain the relationship between viruses and human health from an evolutionary perspective?
According to the book, humans evolved to live in harmony with viruses and other microorganisms rather than in constant battle against them. Dr. Natasha Campbell-McBride's perspective suggests that every viral infection serves a beneficial purpose, acting as a cleanser or purger to remove harmful substances from the body that could cause more serious problems if left unchecked. This symbiotic relationship developed over thousands of generations, creating sophisticated immune responses that work in cooperation with, rather than opposition to, these microorganisms.
The book challenges the common perception of viruses as enemies to be eliminated, instead presenting them as part of a larger community of living things with which humans must maintain balance. Young children's natural instinct to put things in their mouths is described as an evolutionary adaptation for developing immunity, suggesting that our bodies are designed to interact with rather than avoid environmental microorganisms. This perspective fundamentally contradicts the modern medical approach of sterilization and pathogen avoidance.
14. What concerns does the book raise about the lack of long-term vaccine studies?
The book highlights a critical gap in vaccine research through Dr. Stockwell's debate with Dr. Paul Offit, where the absence of comprehensive long-term studies comparing vaccinated and unvaccinated populations becomes apparent. When challenged to provide evidence of long-term vaccine safety and efficacy, Dr. Offit could only produce a 14-day study of 15 children, which the book suggests falls far short of the medical research standard considering "long-term" as ten years or more.
This absence of longitudinal research raises fundamental questions about the scientific basis for current vaccination practices. The book points out that despite vaccines' widespread use since the 1940s, no country has conducted proper long-term studies to establish their safety or effectiveness compared to unvaccinated populations. This gap in knowledge becomes particularly concerning given the increasing number of vaccines recommended for children and the rising rates of chronic conditions.
15. How does the book explain the rise in childhood chronic illnesses in modern times?
The book describes a dramatic shift in childhood health patterns, noting that 20-40% of children now suffer from chronic illnesses, compared to virtually none in previous generations. Looking back to the 1950s, the book notes that asthma was practically non-existent, and children generally remained healthy despite playing in dirt and mud without constant hand washing or sterilization practices. This increase in chronic conditions coincides with the introduction and expansion of childhood vaccination programs.
The pattern of decline in children's health is attributed to several factors, including increased vaccination schedules, environmental toxins, and the disruption of natural immune development through excessive sterilization and medical interventions. The book particularly emphasizes how modern medical practices may interfere with the body's natural immune development processes, creating a generation of children with compromised immune systems and increased susceptibility to chronic conditions.
16. What parallels does the book draw between Oriental and Western medical payment models?
The book presents a striking contrast between traditional Oriental medical practices, where doctors received payment only when their patients remained healthy, and the modern Western system, where compensation comes from treating illness. This fundamental difference in incentive structures led to entirely different approaches to health care. Oriental doctors focused on preventing illness and maintaining health, as their livelihood depended on keeping their patients well.
Modern Western medicine, conversely, generates revenue primarily through treating existing conditions, creating what the book describes as a system designed to "keep you sick by only addressing the symptoms and not the cause of disease." This shift in financial incentives has profoundly influenced how medicine is practiced, moving away from preventive care and natural healing methods toward a model focused on symptom management and pharmaceutical interventions.
17. How does the book explain Dr. Natasha Campbell-McBride's perspective on the role of viruses in human health?
Dr. Campbell-McBride presents a revolutionary perspective on viral infections, describing them as beneficial cleansers that perform necessary functions in the body. She challenges the prevailing "survival of the fittest" theory, instead suggesting that nature works through cooperation. According to her view, every virus that enters the body has been "invited" because it serves a specific purpose in removing substances that could cause more serious health problems if left unaddressed.
This understanding leads to a fundamentally different approach to illness, where symptoms like fever, cold, or flu are seen as blessing rather than curses. The book quotes her explaining that these infections should not be fought or medicalized, as they perform valuable cleansing functions in the body. This perspective aligns with the book's broader argument about the body's inherent wisdom and the importance of working with rather than against natural processes.
18. What significance does the book attribute to the Zypan versus Camel Cigarettes FDA approval story?
The book uses the 1937 case of Zypan and Camel Cigarettes to illustrate the pharmaceutical industry's influence over health regulations. Standard Process attempted to market Zypan, a natural digestive enzyme supplement, but faced FDA prohibition. Meanwhile, Camel Cigarettes received approval to market their product as a digestive aid in the same year, despite their harmful effects, demonstrating what the book describes as the pharmaceutical industry's long-term strategy of creating future patients through harmful products.
This historical example serves to illustrate how regulatory decisions often prioritize pharmaceutical industry interests over public health. The book suggests this case exemplifies a broader pattern where natural healing methods face suppression while potentially harmful chemical interventions receive official sanction, shaping the entire landscape of modern medical practice.
19. How does the book explain the debate between Dr. Jack Stockwell and Dr. Paul Offit regarding vaccine efficacy?
The debate centered on a crucial question about long-term vaccine safety studies, with Dr. Stockwell challenging Dr. Offit to provide evidence of comprehensive research comparing vaccinated and unvaccinated populations. Despite Dr. Offit's initial claim that such studies existed, when pressed for specifics, he could only provide a short-term study of 15 children over 14 days, which the book presents as inadequate for establishing long-term safety or efficacy.
This exchange serves to highlight what the book identifies as a fundamental problem in vaccine science - the lack of proper long-term safety studies despite decades of widespread use. Dr. Offit's position as Chief of Pediatric Diseases and his ownership of vaccine patents adds context to the debate, suggesting potential conflicts of interest in vaccine promotion and research.
20. What role does the book attribute to mercury and aluminum in vaccine formulations?
The book explicitly challenges the common claim that mercury serves as a preservative in vaccines, instead identifying it as a deliberate neurotoxic agent used to provoke an immune response. As the most naturally occurring neurotoxic substance known to man, mercury's inclusion in vaccines serves to shock the nervous system into reacting to the dead or attenuated virus by producing antibodies. The book compares calling mercury a preservative to calling cyanide a preservative, emphasizing its true function as an immune system stimulant.
When vaccine manufacturers claim to remove mercury from their formulations, they typically increase aluminum content or other neurotoxic adjuvants to maintain the shock effect necessary for vaccine function. The book explains that these adjuvants are essential because the immune system would not naturally respond to dead or weakened viruses without this chemical provocation, highlighting how vaccine-induced immunity fundamentally differs from natural immune responses.
21. How does the book explain the body's natural response to infection versus vaccine-induced response?
The natural response follows a precise orchestration where T-cells initiate the immune response by recognizing and attacking pathogens directly. This process creates noticeable symptoms like fever, inflammation, and discomfort - not because the pathogen causes these symptoms, but because the body deliberately generates these responses as part of its defense strategy. Like a well-rehearsed symphony, each component plays its part at exactly the right moment, with B-cells waiting to observe and learn from the T-cells' response before producing targeted antibodies.
In contrast, vaccine-induced immunity attempts to skip this natural sequence by chemically forcing B-cell antibody production without T-cell involvement. Think of it as trying to teach someone to play chess by showing them only the endgame - they might memorize specific moves but miss the strategic understanding that comes from experiencing the full game. The book suggests this shortcut creates an incomplete immune response that may contribute to the rise in autoimmune conditions, as the body never learns the proper sequence of immune responses.
22. What connection does the book draw between vaccination practices and autoimmune conditions?
The book presents a compelling timeline correlation between the widespread implementation of vaccination programs in the 1940s and an unprecedented rise in autoimmune diseases. Before this period, autoimmune conditions were virtually unknown, but they have since become increasingly common, with over 80 different autoimmune diseases now identified. The book explains this phenomenon through the lens of disrupted immune system ordering - when vaccines force antibody production without proper T-cell activation, they create armies of antibodies without proper targeting mechanisms.
The situation resembles giving weapons to soldiers without proper training in identifying enemies - these antibodies, produced through artificial stimulation, may end up attacking the body's own tissues due to lack of proper "training" through the natural immune response sequence. The book particularly emphasizes how this disruption of natural immunity becomes more pronounced with each vaccination, potentially explaining why autoimmune conditions often develop gradually over time with increasing severity.
23. How does the book explain the relationship between gut health and immunity?
The book incorporates Dr. Natasha Campbell-McBride's expertise on the intimate connection between gut development and immune system function, particularly in early childhood. This relationship begins in the womb, where a baby develops in a sterile environment, and continues through the critical first years of life when the digestive system and immune system are learning to work together. The book explains how this development requires exposure to various microorganisms through natural processes, including an infant's instinctive desire to put things in their mouth.
Modern practices of excessive sterilization and early vaccination can interfere with this delicate developmental process, potentially contributing to both digestive and immune system dysfunction. The book draws parallels between the rise in digestive disorders and immune system problems, suggesting they share common roots in disrupted natural development processes. This understanding challenges the common practice of trying to protect children from all possible microbial exposure.
24. What critique does the book offer regarding modern medical symptom suppression?
The book fundamentally challenges the modern medical approach of treating symptoms as problems to be eliminated rather than understanding them as beneficial aspects of the healing process. Using fever as an example, the book explains how symptoms we typically try to suppress - including inflammation, mucus production, and even diarrhea - actually represent the body's intelligent responses to threats. This perspective suggests that suppressing these symptoms might interfere with natural healing processes.
The broader critique extends to the entire framework of modern medicine, which the book suggests has lost sight of the body's innate healing capabilities. Instead of supporting and working with natural processes, modern medicine often attempts to override them with chemical interventions. This approach not only fails to address root causes but may create additional problems by disrupting the body's natural healing mechanisms. The book presents this as a fundamental misunderstanding of how the human body maintains and restores health.
25. How does the book explain children's natural immunization behaviors?
Children's seemingly risky behaviors - playing in dirt, putting objects in their mouths, and avoiding excessive cleanliness - are presented as evolutionarily developed strategies for building proper immunity. The book describes these actions not as problems to be corrected but as instinctive behaviors that help children develop robust immune systems through controlled exposure to environmental microorganisms. This natural process allows for the proper development of both T-cell and B-cell responses in the correct sequence.
Modern parenting practices that emphasize constant sterilization and protection from all microbial exposure may actually interfere with this crucial developmental process. The book suggests that children inherently understand their need to become "one" with the microbial world around them, and that this understanding is so crucial that they will actively resist efforts to prevent this exposure. This perspective challenges the modern emphasis on sterility and suggests that some exposure to environmental microbes is necessary for proper immune development.
26. What perspective does the book offer on the medical industry's approach to preventive medicine?
The book argues that true preventive medicine has been largely abandoned in favor of early detection and disease management strategies that generate ongoing revenue. This shift reflects a fundamental change in medical philosophy, moving away from maintaining health toward managing illness. The comparison to traditional Oriental medical practices, where doctors were paid to keep patients healthy rather than treat diseases, highlights how modern financial incentives have reshaped medical priorities.
The current system, according to the book, discourages true prevention because there's "no money in prevention in western medicine." Instead, the focus has shifted to creating long-term treatment protocols that generate consistent revenue streams. This approach has led to a medical system that excels at managing chronic conditions but shows little interest in preventing their occurrence or addressing their root causes. The book suggests this represents a fundamental betrayal of medicine's original purpose of promoting and maintaining health.
27. How does the book explain the significance of cell-mediated immunity in disease prevention?
Cell-mediated immunity, primarily through T-cell action, serves as the body's front-line defense system and orchestrator of proper immune responses. The book describes this as a sophisticated process where T-cells not only directly combat pathogens but also collect crucial information that guides the entire immune response. This initial response creates symptoms we recognize as illness - fever, inflammation, and discomfort - but these symptoms indicate the proper functioning of our immune system rather than a problem to be suppressed.
The book emphasizes how modern vaccination practices bypass this crucial first step, potentially compromising the entire immune response sequence. By attempting to generate antibodies without proper T-cell activation, vaccines may create an incomplete or improper immune response. This disruption of natural ordering might explain why vaccinated individuals often require booster shots, while natural immunity typically lasts a lifetime. The book suggests that respecting and supporting cell-mediated immunity might be crucial for maintaining long-term health.
28. What concerns does the book raise about current childhood vaccination schedules?
The book expresses serious concerns about the current practice of administering multiple vaccines during infancy and early childhood, particularly before the immune system has fully developed. It points out that babies cannot produce their own antibodies until around twelve months of age, yet vaccination programs often begin much earlier. This timing creates a potential mismatch between the body's developmental capabilities and medical interventions, possibly contributing to rising rates of childhood chronic conditions.
The scale of vaccination has also expanded dramatically, with children now receiving over 150 inoculations between birth and age 18. The book suggests this represents an unprecedented experiment with children's developing immune systems, conducted without proper long-term safety studies. Of particular concern is the cumulative effect of multiple vaccines and their adjuvants on neurological development and immune system function, especially given the dramatic increases in conditions like autism and other developmental disorders.
29. How does the book explain the relationship between environmental toxins and immune system function?
The book presents environmental toxins as part of a larger pattern of immune system challenges that includes vaccination practices, poor nutrition, and other modern environmental exposures. These combined factors create what the book describes as a perfect storm of immune system disruption, where natural defense mechanisms become increasingly compromised over time. The situation becomes particularly concerning when these environmental exposures occur during critical developmental periods in early childhood.
The compounding effect of these various exposures may explain why we're seeing unprecedented rates of immune dysfunction and chronic illness. The book suggests that adding vaccination-related neurotoxins to an already toxic environment may overwhelm the body's natural detoxification and defense mechanisms. This perspective emphasizes the importance of considering the total burden on the immune system rather than viewing each exposure in isolation.
30. What solution does the book propose for supporting natural immunity?
The book advocates for a return to understanding and supporting the body's innate healing capabilities rather than attempting to override them with chemical interventions. It specifically mentions the "6-3-6 Immune Triad Protocol," which includes calcium lactate, whole food vitamin C, and essential fatty acids, as a way to support rather than suppress natural immune functions. This approach aims to provide the body with the nutritional tools it needs to maintain proper immune responses.
The broader solution involves a fundamental shift in how we think about health and immunity. Rather than viewing microorganisms as enemies to be eliminated, the book suggests embracing them as necessary partners in human health. This includes allowing natural immune responses to run their course when appropriate, supporting the body's healing processes with proper nutrition, and being more selective about medical interventions that might disrupt natural immunity. The goal is to work with rather than against the body's innate intelligence.
I appreciate you being here.
If you've found the content interesting, useful and maybe even helpful, please consider supporting it through a small paid subscription. While everything here is free, your paid subscription is important as it helps in covering some of the operational costs and supports the continuation of this independent research and journalism work. It also helps keep it free for those that cannot afford to pay.
Please make full use of the Free Libraries.
Unbekoming Interview Library: Great interviews across a spectrum of important topics.
Unbekoming Book Summary Library: Concise summaries of important books.
Stories
I'm always in search of good stories, people with valuable expertise and helpful books. Please don't hesitate to get in touch at unbekoming@outlook.com
For COVID vaccine injury
Consider the FLCCC Post-Vaccine Treatment as a resource.
Baseline Human Health
Watch and share this profound 21-minute video to understand and appreciate what health looks like without vaccination.